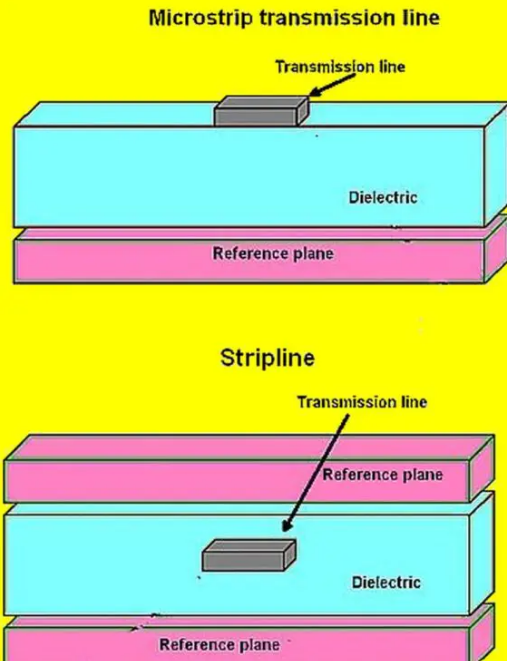
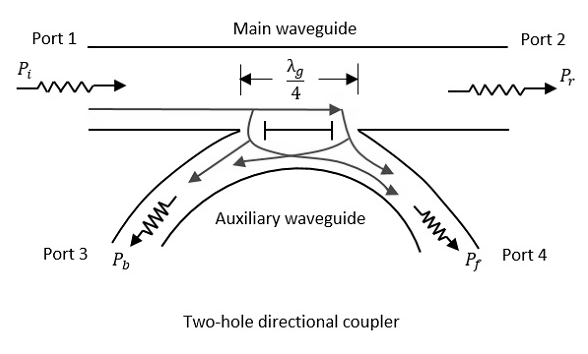
What is the waveguide effect
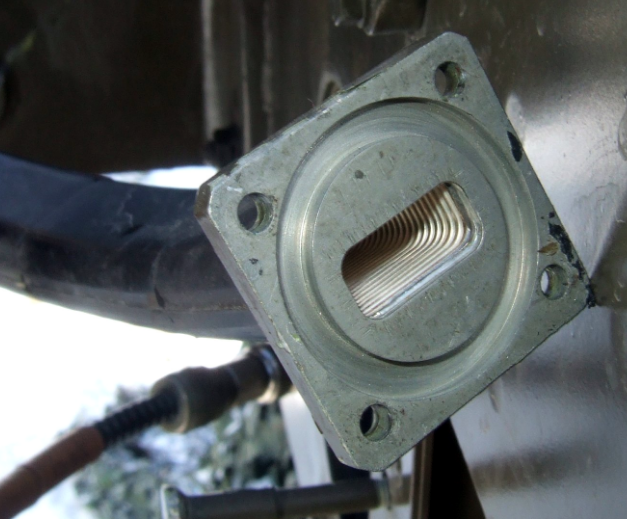
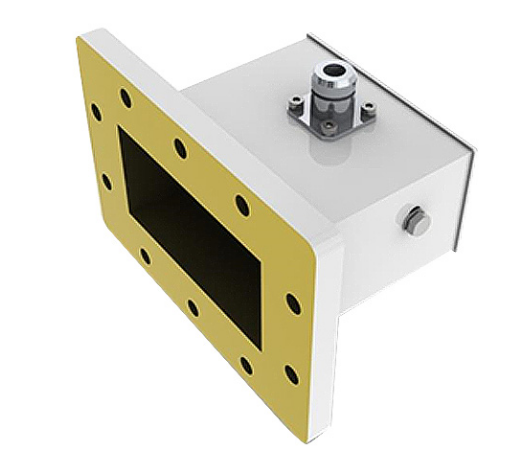
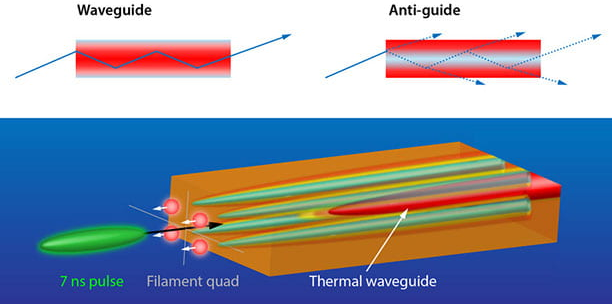
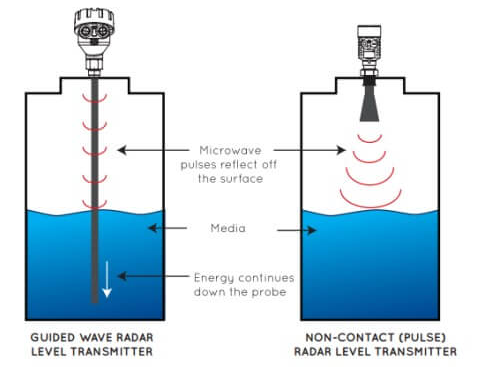
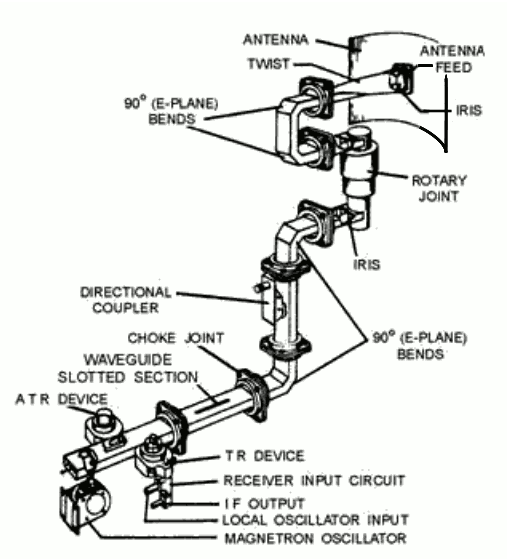
The waveguide effect directs electromagnetic waves through a medium, minimizing loss, as in optical fibers with 0.2 dB/km attenuation. Definition of Waveguide Effect The waveguide effect is an essential phenomenon, where electromagnetic waves, light, or sound are confined to a specific direction and distance in a medium. Basically, that means waveguides can be used to […]
What is the waveguide effect Read More »